Why Is My Cat Breathing Rapidly: Understanding Causes and When to Seek Help
By: Elizabeth Rikas

The information in this article is intended to educate cat parents and is not a substitute for veterinary guidance. In case of any concerns about your cat’s health, please talk with your veterinarian.
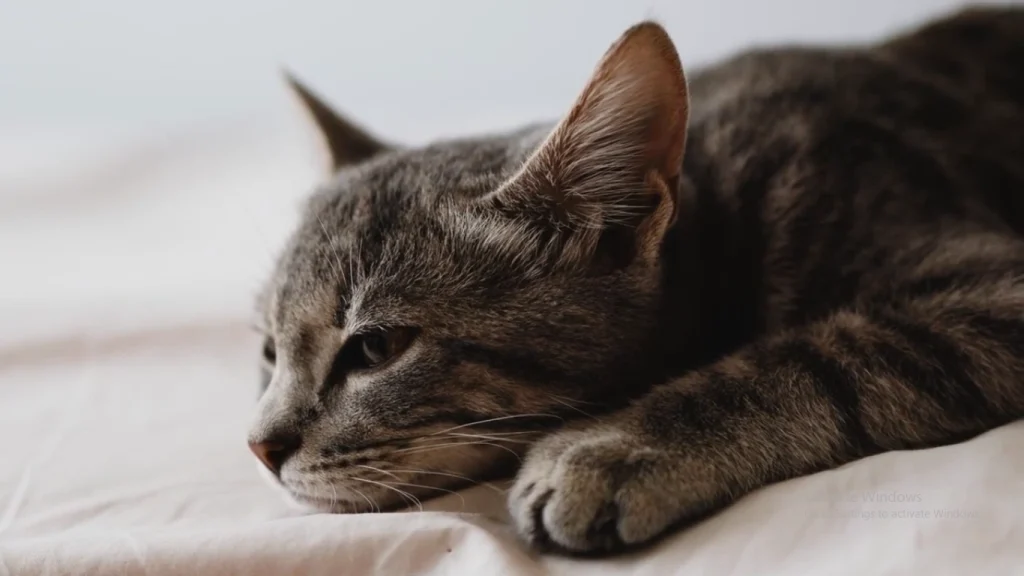
Rapid breathing in cats can be alarming for pet owners. There are several reasons why a cat may breathe rapidly, ranging from normal responses to stress or exercise to more serious health issues. It’s important for owners to understand these causes to ensure their cat’s well-being.
While some instances of fast breathing are harmless, persistent rapid breathing can indicate health problems that require attention. Observing other symptoms, such as lethargy or difficulty breathing, can help identify when a visit to the veterinarian is necessary.
Understanding the factors that contribute to rapid breathing is the first step in addressing any potential issues. By being informed, owners can take appropriate action to keep their furry friends healthy and happy.
Key Takeaways:
- Rapid breathing may be normal during stress or exercise.
- Persistent rapid breathing requires veterinary attention.
- Monitoring other symptoms can help identify health issues.
Click to explore: How To Make Cats’ Fur Softer
Understanding Normal Cat Breathing
Cats have specific breathing patterns that are important to recognize. Knowing what normal breathing looks like can help in identifying any potential issues. This section covers normal respiratory rates and how to recognize abnormal patterns in a cat’s breathing.
Normal Respiratory Rates in Cats
A typical cat at rest breathes between 20 to 30 times per minute. This is considered a normal respiratory rate. Factors like age, weight, and activity level can affect these numbers slightly.
To measure your cat’s breathing rate, observe them in a calm state. Count the number of breaths they take in one minute. If the rate is consistently above 30 breaths, this might indicate you could be dealing with tachypnea, or rapid breathing, which can be a sign of stress or health concerns.
Identifying Abnormal Breathing Patterns
It is essential to notice any changes in a cat’s breathing. Abnormal patterns can include increased rapid breathing, labored breathing, or panting.
Some signs of concern are:
- Tachypnea: Rapid breathing while resting.
- Open-mouth breathing: This can indicate distress.
- Change in sounds: Noisy breathing or wheezing could signal respiratory problems.
If a cat displays any of these abnormal breathing patterns, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian promptly. Quick attention can help identify any serious health issues.
Causes of Rapid Breathing in Cats
Rapid breathing in cats can arise from various factors. Understanding these causes is essential for pet owners to know when to seek veterinary care. Significant causes include stress and anxiety, specific medical conditions, and environmental factors like heatstroke or overexertion.
Stress and Anxiety-Induced Tachypnea
Cats can experience rapid breathing due to stress or anxiety. Common triggers include loud noises, unfamiliar environments, or the presence of other pets or people. When a cat feels threatened, its body may respond with a fight-or-flight reaction, increasing heart rate and breathing rate.
Signs accompanying anxiety can include vocalization, hiding, or changes in eating habits. It’s crucial for owners to create a calm environment. Using calming products or safe spaces can help reduce anxiety.
Medical Conditions Leading to Dyspnea
Many medical issues can cause rapid breathing in cats, also known as dyspnea. Conditions like heart disease, respiratory infections, or anemia can result in increased efforts to breathe. These health problems lead to inadequate oxygen levels in the bloodstream, prompting the cat to breathe faster.
Symptoms may include coughing, lethargy, and difficulty breathing when at rest. A veterinarian should evaluate any cat showing these signs to diagnose and treat underlying conditions promptly.
Heatstroke and Overexertion Effects
Heatstroke is a serious condition that can lead to rapid breathing. Cats are susceptible to overheating, especially in high temperatures or during vigorous play. As the cat’s body tries to cool down, it increases its breathing rate to enhance heat loss.
Signs of heatstroke include excessive panting, drooling, and lethargy. Owners must monitor their cats during hot weather and provide ample water and shade. If a cat shows signs of overheating, immediate cooling measures are vital along with veterinary assistance.
Click to explore: Split Claws In Cats
When to Seek Veterinary Care
Rapid breathing in cats can signal a serious issue. Recognizing when to seek veterinary care is crucial for the health of the pet. Evaluating symptoms properly can help determine the urgency of the situation.
Evaluating the Severity of Symptoms
When a cat exhibits rapid breathing, owners should first evaluate the severity. They should look for additional symptoms like wheezing, which might indicate blocked airways, or dyspnea, a term for difficulty breathing. Observing the cat’s general behavior is important.
For example, if the cat is lethargic, refuses to eat, or seems distressed, these signs may suggest a more serious condition. The normal respiratory rate is between 20-30 breaths per minute. Any rate significantly above this warrants immediate veterinary attention. Keeping track of whether the breathing is shallow or accompanied by gasps can also provide vital information.
Click to explore: Can Cats Eat Pumpkin?
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Veterinarians may perform several diagnostic procedures to identify the issue causing rapid breathing. Common tests include X-rays to view the lungs and airways, blood tests to check for infections or other underlying conditions, and ultrasound if heart issues are suspected.
In cases of tachypnea, it helps to provide the veterinarian with a detailed history of the cat’s symptoms. This information can guide decisions on which tests are necessary. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment. Owners should not delay seeking help, as many breathing issues can progress quickly if left untreated.
Click to know: Siberian Cat Size Comparison
Treatment and Management
When a cat is breathing rapidly, it is crucial to take action for their health and comfort. This section covers immediate steps to address rapid breathing, ongoing care, and ways to prevent future issues.
Immediate Actions for Rapid Breathing
If a cat is breathing rapidly, the first step is to remain calm. This helps the cat feel more secure.
- Assess the Environment: Ensure the cat is in a quiet, stress-free area. Loud noises or crowds can increase anxiety.
- Check for Obvious Issues: Look for signs of injury or distress. If the cat has any visible wounds or other symptoms, note them.
- Contact a Veterinarian: Rapid breathing can indicate serious health problems. Calling a veterinarian immediately for advice is critical. They may advise bringing the cat in for examination.
- Do Not Delay: If there are signs of severe breathing difficulty or the cat is gasping, seek emergency care without hesitation. Quick actions can make a difference in outcomes.
Long-Term Care and Monitoring
After addressing immediate concerns, monitoring the cat’s condition is essential.
- Regular Vet Check-ups: Schedule routine veterinary visits. Regular check-ups help catch underlying conditions early.
- Observe Behavior: Owners should watch for changes in breathing patterns. Consistent rapid breathing can be a sign of chronic conditions needing management.
- Managing Health Issues: If the cat has diagnosed health problems such as asthma or heart disease, follow the vet’s treatment plan carefully. Medication adherence is vital.
- Maintain a Calm Environment: Stress can exacerbate breathing issues. Provide a safe space where the cat feels at ease.
Preventative Measures and Tips
Taking steps to prevent rapid breathing is crucial for overall health.
- Healthy Diet: Provide a balanced diet that supports respiratory health. Consult the veterinarian for dietary recommendations.
- Regular Exercise: Encourage playtime to keep the cat active. This can help maintain a healthy weight, which affects respiratory function.
- Avoid Smoke and Pollutants: Keep cats away from smoke, strong odors, or chemicals. These can irritate the lungs and lead to breathing problems.
- Manage Weight: Keeping the cat at a healthy weight reduces stress on the respiratory system. Regular weighing is recommended to monitor changes.
By following these actions, owners can effectively manage and reduce the risk of rapid breathing in their cats.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cats can breathe rapidly for various reasons, including health concerns and environmental factors. Understanding these causes can help owners make informed decisions about their pet’s well-being.
Conclusion
Rapid breathing in cats can stem from various causes, from stress and anxiety to serious health conditions like heart disease or respiratory infections. While occasional fast breathing may be normal, persistent or labored breathing warrants immediate veterinary attention. By staying observant and proactive, cat owners can ensure their pets receive timely care, safeguarding their health and well-being.
Understanding your cat’s normal breathing patterns and recognizing abnormalities is key to addressing potential issues early. Whether it’s managing stress, preventing heatstroke, or seeking medical intervention, informed decisions can make a significant difference. A vigilant approach helps keep your feline companion healthy, happy, and thriving.

About the Author
Elizabeth Rikas
Elizabeth is a passionate advocate for feline health and well-being, drawing from her years as a dedicated pet parent to three cats—Gypsy, Swan, and Alfred—and her invaluable experience volunteering at animal shelters. A seasoned writer with a lifelong love for cats, Elizabeth began sharing her insights in her teens and has since contributed extensively to platforms focused on feline care. Through her expertise and heartfelt dedication, she empowers pet owners with practical advice and research-backed knowledge to nurture their furry companions.